AWS NAT Gateway Cost? Key Pricing Factors & Tips To Reduce
Are you wrestling with the intricacies of cloud infrastructure costs? Understanding and optimizing the expenses associated with Network Address Translation (NAT) Gateways is crucial for any organization leveraging Amazon Web Services (AWS).
In the dynamic world of cloud computing, managing costs efficiently is not merely a financial prudence; it's a strategic imperative. As businesses increasingly rely on cloud services for their operations, a comprehensive understanding of the pricing models and cost optimization strategies for core services like NAT Gateways becomes paramount. This article delves into the nuances of AWS NAT Gateway pricing, providing a detailed analysis of the cost factors, potential savings opportunities, and practical strategies for effective cost management. We will explore various aspects of NAT Gateways, from their fundamental functions to advanced optimization techniques. This information is critical for IT professionals, cloud architects, and financial decision-makers aiming to strike the right balance between performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
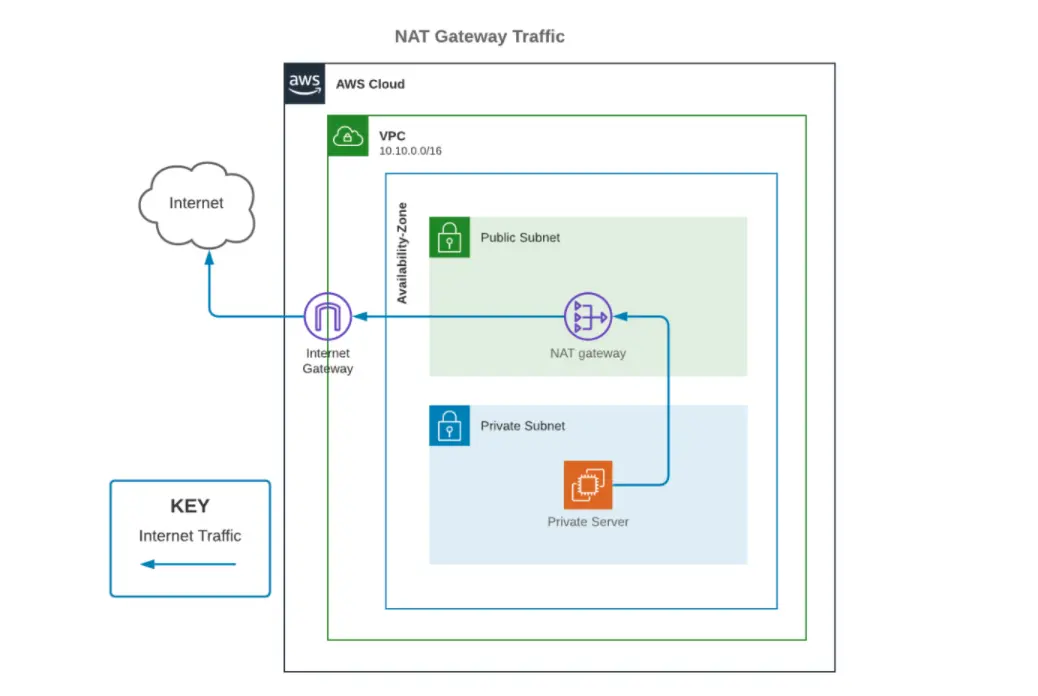
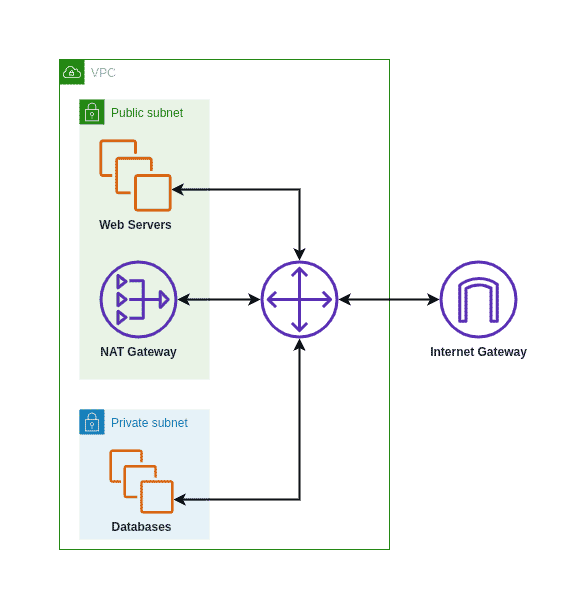
For those seeking to connect instances in a private subnet to the internet, a NAT Gateway provides a vital service. By allowing outbound internet access for instances in a private subnet, NAT Gateways offer a secure and manageable solution. However, with convenience comes cost. The pricing structure of NAT Gateways involves several components, including a per-hour charge for the gateway's availability, data processing fees, and data transfer charges. It's important to note that these costs can vary depending on the region and the volume of data processed. For example, in certain regions, the hourly rate for a NAT Gateway is $0.045, with additional charges for data processing and data transfer, and these costs can add up significantly over time.
The AWS documentation highlights that these costs are based on three main factors: a fixed hourly rate, data processing charges (applied per gigabyte processed), and standard data transfer fees. To ensure cost efficiency, it's important to regularly monitor the usage of your NAT Gateways and analyze the data transfer patterns. By identifying areas where you can optimize traffic flow or use more cost-effective alternatives like VPC endpoints, you can significantly reduce your cloud expenses. Also, it is a good practice to understand the difference between NAT instances and NAT Gateways. While NAT instances are essentially EC2 instances running a service in a public subnet, NAT Gateways are managed services that offer higher availability and scalability. Although NAT Gateways come with a higher hourly cost, they often prove to be more reliable and easier to manage for larger workloads. Moreover, if your application primarily interacts with AWS services that support interface endpoints or gateway endpoints, consider using these endpoints. This strategy helps reduce costs and improves the security of your infrastructure.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Component | AWS NAT Gateway |
| Description | Allows instances in a private subnet to connect to the internet. |
| Primary Function | Facilitates outbound internet access for instances within a private subnet while maintaining security and manageability. |
| Pricing Model |
|
| Cost Factors |
|
| Cost Optimization |
|
| Management |
|
| Alternative | NAT Instance (EC2 instance running a NAT service) |
| Reference | AWS VPC Pricing Page |
To further illustrate the cost implications, consider a scenario where you've set up a NAT Gateway, and an EC2 instance routes traffic through it to the internet. If this instance then transmits 1 GB of data to an Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) bucket, you'll incur costs based on the hourly rate of the NAT Gateway and data processing fees. Data transfer charges will also apply for the outbound data transfer from your VPC to the internet. The total cost will depend on the specific region and the volume of data transferred.
Deploying a NAT Gateway in each Availability Zone (AZ) is generally recommended to ensure high availability and reduce latency. Doing so helps to maintain optimal performance, especially in applications with cross-AZ traffic. Also, if the NAT Gateway fails, any connections with resources using that gateway will also fail. By strategically deploying NAT Gateways across multiple AZs, you can build a more resilient infrastructure.
If you find that your AWS resources are sending or receiving a significant volume of traffic across Availability Zones, then it's imperative to ensure that the resources and the NAT Gateway are within the same Availability Zone. Alternatively, create a NAT Gateway in each AZ with the necessary resources. For those services that support interface endpoints or gateway endpoints, using them would lead to cost-effective and secure infrastructure. In such situations, utilizing VPC endpoints can significantly reduce costs. You can also use VPC endpoints and NAT Gateways at the same time, the best strategy depends on factors, such as the amount of traffic to external services and the number of AWS services being used.
It's critical to understand that the cost structure may change over time, so it's important to stay updated with the latest AWS pricing. You can use the AWS Pricing Calculator to estimate and manage your NAT Gateway costs. This tool allows you to input various factors and determine the associated costs, which helps in planning and optimizing your budget. Remember that data processing costs are based on the amount of data the NAT Gateway processes, regardless of its source or destination. However, data transfer costs will vary depending on the data volume and the specific data transfer scenario.
As stated, NAT Gateways are charged per hour, plus data processing and data transfer charges. A fixed hourly rate is applied for each hour that the NAT Gateway is provisioned and available. Data processing costs are based on the amount of data processed by the NAT Gateway. These costs apply regardless of the traffics source or destination. And the data transfer costs are the usual costs to move data between an EC2 instance and the internet. The specific pricing model differs across regions. AWS provides full details on the VPC pricing page.
There are various techniques to mitigate the costs associated with NAT Gateways. For example, if your resources are sending or receiving substantial traffic between Availability Zones, make sure that both the resources and the NAT Gateway are in the same AZ. You can also consider creating a NAT Gateway in each AZ with the required resources. If most traffic goes to AWS services that support interface or gateway endpoints, creating an interface endpoint or a gateway endpoint for these services could be an option.
If you no longer need a NAT Gateway, removing it is straightforward. You can delete the NAT Gateway using the AWS Management Console, the Command Line Interface (CLI), or the API. Also, if a public NAT Gateway is deployed in a private subnet (although the AWS console allows this), the NAT Gateway will not be able to route traffic to the Internet Gateway. So, you should be very careful when configuring your NAT Gateways.
Understanding the pricing structure of AWS services such as NAT Gateways is crucial for effective cloud cost management. This includes a fixed hourly rate and charges for data processed and transferred. By optimizing your infrastructure and staying updated on pricing changes, you can create a cost-efficient and scalable environment.
Different cloud providers have distinct pricing models for their NAT services, and understanding these differences is vital for budgeting and optimizing costs. In AWS, NAT Gateway costs have two primary components: an hourly rate and data processing charges. Data transfer charges apply if the NAT Gateway is used, and the costs will depend on the region and data volume. To reduce costs, monitor NAT Gateway logs to identify and address unexpected traffic or excessive data transfer. Optimize your infrastructure and select the most cost-effective solutions.
If you are using ECS Fargate, with two subnets in different zones, and using a NAT Gateway to access services such as CloudWatch, ECR, and S3, remember that switching to VPC endpoints may be cheaper and more secure. Evaluate VPC endpoint pricing to see if it aligns with your cost and security needs. However, be aware of potential cost implications, as NAT Gateways are charged per hour and per GB processed. If your application transfers 1 GB of data from an EC2 instance through the NAT Gateway to S3, and the transfer happens within the same region, you won't be charged for data transfer from EC2 to S3. However, youll incur NAT Gateway charges and data processing fees.
To reduce the cost, make sure the resources that need to transfer data are in the same network and availability zone. Also, remember that if your application runs across multiple Availability Zones, be mindful of the data transfer costs between them. It's often more cost-effective to have resources and their associated NAT Gateways within the same AZ. This architecture will optimize both costs and performance.
To gain further insights and make informed decisions about your AWS infrastructure costs, explore the following resources:
- AWS VPC Pricing Page: Comprehensive details on NAT Gateway and other VPC-related pricing.
- AWS Pricing Calculator: Estimate and manage your NAT Gateway costs.
- AWS Documentation: Official documentation providing detailed information on NAT Gateway features, configuration, and best practices.
- AWS Blogs and Articles: Stay updated with the latest insights, cost optimization strategies, and announcements.
To summarize, effective management of NAT Gateway costs in AWS involves a combination of understanding the pricing model, monitoring usage, optimizing traffic flow, and utilizing cost-effective alternatives such as VPC endpoints. By adopting these strategies, businesses can achieve significant cost savings and create a more efficient cloud infrastructure.